Surface coating

Are you an existing customer or do you want to contact us in a different matter? We look forward to hearing from you and will get back to you as soon as possible.
Alternatively, you may want to contact directly one of our locations or our holding company.
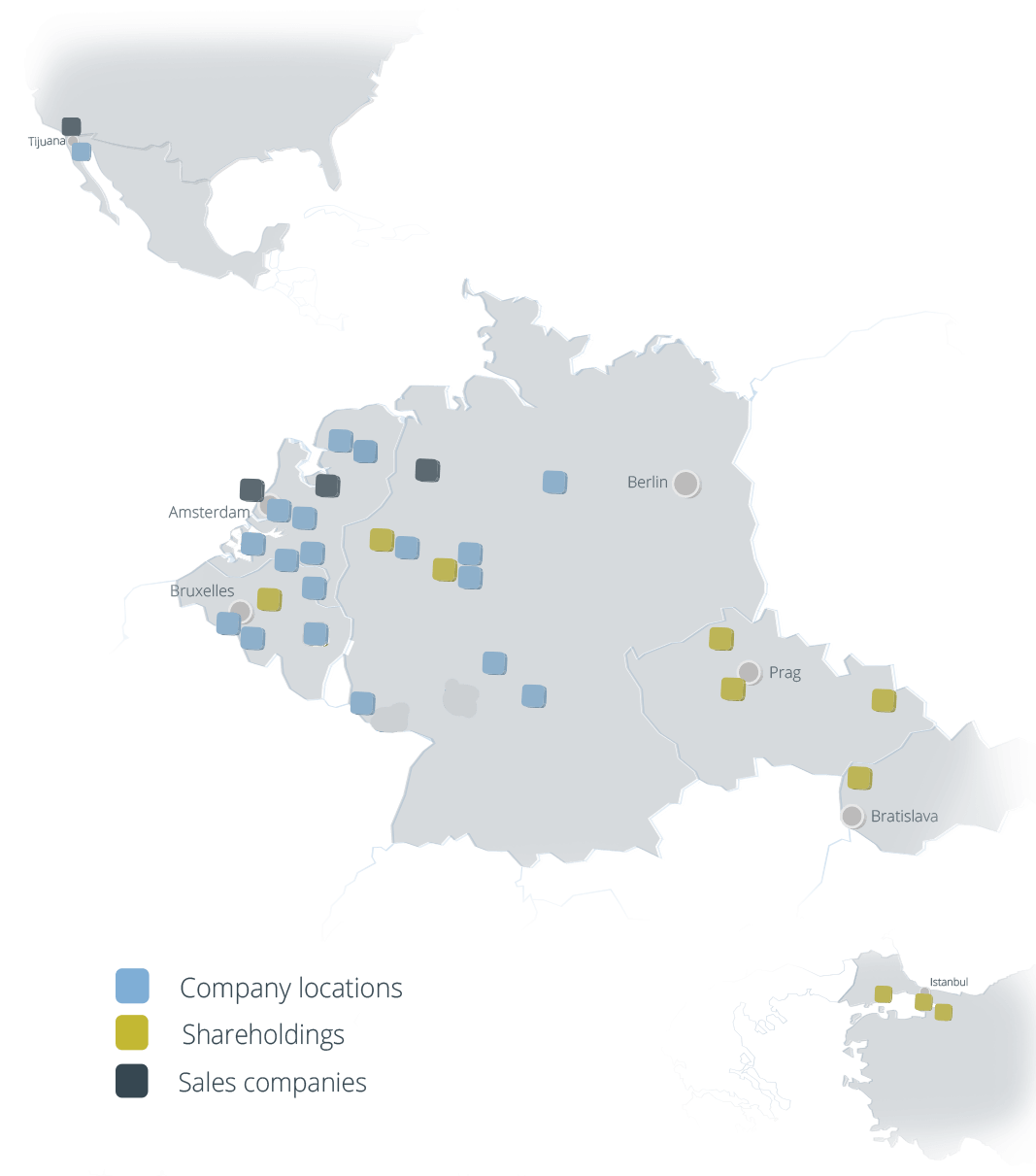
Locations
The Coatinc-Network
Slovakia
Netherlands
- Alblasserdam / NL
alblasserdam@coatinc.com - Amsterdam / NL
amsterdam@coatinc.com - Barneveld / NL
nederland@coatinc.com - De Meern / NL
demeern@coatinc.com - Groningen / NL
groningen@coatinc.com - Groningen – Pulverbeschichtung / NL
cgr.verkoop@coatinc.com - Mook / NL
mook@coatinc.com - Mook – PreGa / NL
prega.nl@coatinc.com - Roermond / NL
roermond@coatinc.com - Scherpenzeel / NL
anox@coatinc.com
For enquiries regarding marketing or press matters, please use the following contacts:
Marketing & Press
The Coatinc Company Holding GmbH
Hüttenstraße 45
57223 Kreuztal
Your contact person:
Anna-Maria Ademaj
marketing@coatinc.com
Holding
Headquarter
The Coatinc Company Holding GmbH
Carolinenglückstraße 6-10
44793 Bochum, Germany
Phone: +49 234 52905-0
Fax: +49 234 52905-15
Encyclopedia
Surface coating
Surface coating
Pretreatment
All surface technology requires the substrate surface to be pretreated. This, in turn, is dependent on several factors – for example type and composition of the base material (metals, non-ferrous metals, etc.), type and extent of impurities (unwanted separation layers) and so-called fault zones caused by processing. This occurs, for example through cleaning, greasing, staining, etching or creating conversion coats (phosphating and other chemical-thermal procedures).
Application of surface coating
Applying the material with specified properties to the substrate (material) and the production of a bond which fulfils the defined properties, for example the mechanical behaviour (firmness and toughness) is known as the application. The applied coat of material fulfils specific properties which go beyond the mechanical properties such as corrosion resistance and wear resistance, power transmission (coefficient of friction in steelwork)… right up to optical and aesthetic demands. In order to create a well functioning and operational bond, sufficient adherence (grip) of the coating is required. This is particularly relevant in the case of mechanical tension, for example due to thermal expansion. There are three different kinds of coating: metal coating, non-metal organic and non-metal non-organic coatings.
Metal coatings
Metal coatings can be coated using ECD (electrochemical metal deposition), by deposing metallic coats from the gas phase or also by hot-dipping (one of the oldest techniques of creating metallic casings – for example hot-galvanising, hot-dip tinning, hot-dip aluminising), by metal spraying (flame spraying, electric arc spraying, plasma spraying), by plating (roll cladding, explosion cladding) or also through chemical-thermal procedures (aluminising, inchromating, sheradizing).



